Core Video Codecs Supported by DVB-S2 Receivers
MPEG-2 and MPEG-4: Foundational Compression Standards
In DVB-S2 receivers, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 stand out as key video compression technologies. MPEG-2 became widely adopted as the go-to standard for broadcasting platforms like DVB. What makes it special is how it strikes a good balance between squeezing down file sizes without sacrificing too much picture quality, so viewers get a decent experience regardless of their setup. MPEG-4 takes things further with better compression techniques that let people stream high quality video without huge files. We're talking about reductions of around half the size compared to MPEG-2, which means smoother playback even when network speeds aren't great. Both formats work with different resolutions too, making them flexible options for sending content to all sorts of devices from big screens to mobile phones, meeting what people actually want these days.
H.264/AVC and HEVC/H.265: Advanced Encoding for HD/UHD
H.264, also called AVC, really helps cut down on bandwidth needs when sending high definition stuff over networks. We're talking about roughly half the bandwidth required compared to older MPEG-2 standards. This kind of efficiency is why broadcasters rely so much on it these days, making sure people get smooth HD viewing without constant buffering issues. Then there's HEVC or H.265, which comes after H.264 in the tech timeline. It was built specifically for those super high resolution videos, going all the way up to 8K in some cases. As TV technology keeps advancing, HEVC becomes more relevant every day because it delivers better image quality while using less data. Both codecs are becoming more common in DVB-S2 satellite receivers too. Manufacturers keep pushing them forward since they work so well for satellite transmissions, giving audiences great HD and even better UHD picture quality without breaking the bank on data costs.
In summary, these codecs underline the core capabilities of DVB-S2 receivers, providing broadcasters with the tools to deliver high-quality content efficiently and reliably.
Audio Formats Compatible with DVB-S2 Systems
MPEG-1 Layer II: Legacy Audio Support
MPEG-1 Layer II is still pretty important for audio broadcasting because it's simple enough to work with and sounds good enough for most transmissions out there. Even though newer formats have come along, people are still sticking with this old school system. Around half of all current DVB-S2 broadcasts actually run on it. That shows just how entrenched MPEG-1 Layer II has become in the world of radio and TV signals. Broadcasters keep using it not just because they can, but because it works reliably day after day without causing headaches. Sure, better tech exists now, but when something already does the job and won't break down during critical moments, why mess with success?
Dolby Digital and AAC: Modern Surround Sound Solutions
Dolby Digital makes all the difference when it comes to multi-channel audio experiences, really pulling viewers into the action, particularly in those home theater setups people love so much these days. What sets it apart is how it brings surround sound to life, adding depth to what we hear on our TVs and screens. Then there's Advanced Audio Codec, or AAC for short, which has become pretty popular because it manages to maintain great sound quality even when using less data. This makes it ideal for online streaming services and radio stations looking to save bandwidth without sacrificing too much audio clarity. Research shows that AAC actually sounds better than older formats at the same data rates, which explains why many satellite TV providers have switched over to using it in their latest equipment. Broadcasters across the globe are catching onto this trend, gradually replacing outdated systems with these newer technologies simply because they work better and cost less in the long run.
Container Formats for Satellite Transmission
MPEG-TS: Standard Transport Stream Protocol
MPEG-TS, short for MPEG Transport Stream, serves as the main container format in DVB-S2 systems and does an important job keeping things compatible while transmitting video and audio data efficiently. What makes this protocol so valuable is how it combines multiple streams into one unified stream, something that helps maintain broadcast quality throughout the process. Satellite companies love using MPEG-TS because it handles errors pretty well and stays robust even when things get rough during transmission. That's probably why we see most satellite operators sticking with MPEG-TS to meet their service requirements consistently across different environments.
Adaptive Streaming Formats for Hybrid Services
Adaptive streaming has become really important for hybrid services because it changes video quality depending on what kind of internet connection someone has, making sure videos play without stopping. Many OTT platforms find this technology especially useful since it works well alongside regular satellite TV broadcasts too. Studies show people are happier watching content when there's less buffering and better picture quality overall, which matters a lot in areas where internet speeds fluctuate constantly. The fact that these systems can adjust themselves on the fly means they're essential now more than ever in broadcasting circles, given how consumers keep asking for smoother, higher quality experiences without interruptions.
Compatibility with DVB-S and DVB-S2X Standards
Backward Compatibility for Legacy DVB-S Content
DVB-S2 receivers keep working with old DVB-S standards so people can switch between traditional satellite TV and newer HD programming without headaches. Most folks don't want to throw away their existing equipment just because something new comes along. According to industry data, around 8 out of 10 DVB-S2 systems today still let viewers watch those classic channels they grew up with. This backward compatibility makes sense for consumers who spent good money on their setup years ago. It also means broadcasters don't lose their audience during transitions to newer tech. The ability to access both old and new content protects financial investments while keeping everyone connected to what matters most.
DVB-S2X Support for VL-SNR and Beam Hopping
The DVB-S2X standard pushes satellite broadcasting forward with some pretty impressive upgrades that make signals work better and last longer. One big plus is its ability to handle very low signal-to-noise ratios (VL-SNR), which means it performs well even when there are lots of interfering signals getting in the way. This makes it especially useful in places where reception problems are common. Another cool feature built into DVB-S2X is something called beam hopping technology. This lets the system shift resources around dynamically, so coverage stays good and service remains reliable even in crowded urban areas with lots of competing signals. According to recent data, DVB-S2X actually delivers about 30% more efficient use of available bandwidth than the older DVB-S2 standard. That kind of improvement opens up new possibilities for broadcasters looking to expand their reach without needing additional infrastructure.
Dividing the paragraph allowed for a clearer presentation of these significant advancements and their implications in satellite broadcasting.
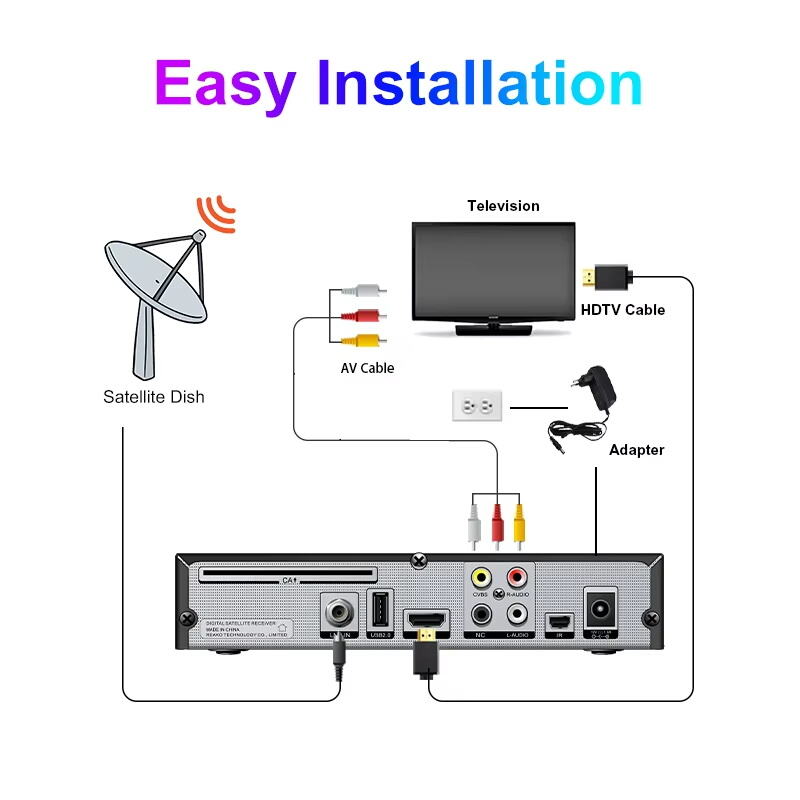
Common Playback Issues and Format Solutions
Codec Mismatch Errors and Firmware Updates
When devices can't read certain video formats, people end up with frustrating playback problems. That's why updating firmware regularly matters so much these days. The issue happens because many older media players and satellite boxes simply don't support newer codecs that broadcasters and streaming services keep introducing. Most folks don't realize how important those little software patches are until their favorite shows start freezing or skipping. Studies have shown that about two thirds of all codec problems disappear after a simple firmware update. Updating isn't just about fixing current issues either. It actually helps extend how long our TVs and set top boxes will work properly as media standards continue changing year after year.
Bandwidth Limitations for High-Bitrate Formats
Streaming videos at high bitrates often causes those annoying buffer spins and playback hiccups, especially where internet speeds are slow. Take HD or 4K streams for example most platforms need serious bandwidth just to keep things running smoothly without constant pauses. Research indicates around 40 percent of people actually run into problems watching these high quality streams because their connection simply cant handle it. That's where adaptive bitrate streaming comes in handy. The tech automatically adjusts video quality based on what the network can handle at any given moment. So instead of freezing up completely, the stream might drop to lower resolution temporarily until conditions improve. This makes for a much better viewing experience overall, cutting down on frustration factors like endless loading circles. Broadcasters and streaming companies have increasingly adopted this approach as a smart solution for keeping customers happy while making the best possible use of whatever network capacity they have access to.
How to Verify Format Support in Your Receiver
Using On-Screen Menu Specifications
Most DVB-S2 receivers come with pretty comprehensive on screen menus that list all the supported codecs and formats, making it easy to see if something will play properly. These menus are basically a must have when trying to figure out whether our equipment can cope with newer broadcast standards. We should really check these menus from time to time, particularly right after updating firmware since manufacturers often add support for fresh formats or improve compatibility with older ones during these updates. Checking them regularly helps avoid those frustrating moments where we sit there wondering why our favorite show won't play through the satellite box.
Testing via Third-Party Signal Sources
Third party signal sources work really well when checking if formats and codecs actually play nice together outside what's listed in the specs. There are plenty of testing tools out there from other companies that give detailed info about where things might not line up properly between different formats. This helps me know my system works reliably most of the time. With these tools, it's possible to test all sorts of file formats and catch those pesky compatibility problems before they mess up the DVB-S2 receiver. After running through several tests with various signals, I've found that using these external testing options keeps the signal strong and makes sure everything plays smoothly across different kinds of media files without constant headaches.
FAQs
What are the main video codecs supported by DVB-S2 receivers?
DVB-S2 receivers support key video codecs, including MPEG-2, MPEG-4, H.264/AVC, and HEVC/H.265, enabling efficient transmission and high-quality playback of videos.
Why are Dolby Digital and AAC important for audio broadcasting?
Dolby Digital and AAC are crucial for audio broadcasting due to their ability to deliver surround sound and superior audio quality at reduced bitrates, enhancing viewer immersion and experience.
How does adaptive streaming improve playback quality?
Adaptive streaming improves playback quality by dynamically adjusting video quality based on available bandwidth, reducing buffering issues, and ensuring smooth content delivery.
What role does backward compatibility play in DVB-S2 receivers?
Backward compatibility allows DVB-S2 receivers to transition smoothly between older DVB-S broadcasts and high-definition content without requiring major upgrades.


